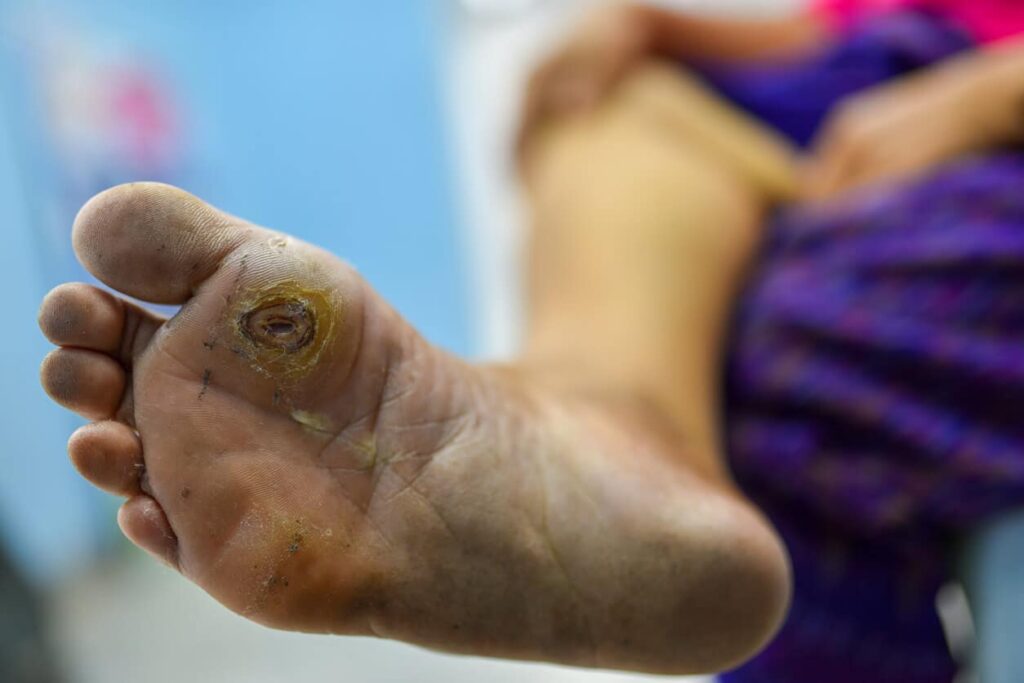
Diabetic gangrene is a serious complication that develops when high blood sugar levels and poor circulation lead to tissue death. Patients with diabetes are particularly vulnerable because their blood vessels often become damaged over time, reducing oxygen and nutrient flow to the extremities. When wounds or infections fail to heal properly, gangrene may develop, most commonly in the feet and legs. The condition can present in different forms, including dry gangrene, which results from poor circulation; wet gangrene, which is associated with infection; and gas gangrene, caused by specific bacteria releasing toxins. Each form requires urgent medical attention to prevent life-threatening complications. Early warning signs include skin discoloration, foul odor, severe pain, numbness, and swelling in the affected area. Recognizing these symptoms promptly allows patients to seek medical help before the infection spreads, improving the chances of effective orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene.
The Role of Orthopedic Care in Managing Diabetic Gangrene
Orthopedic specialists play a critical role in evaluating and treating diabetic gangrene, especially when bones and joints are involved. They carefully assess the extent of tissue and skeletal damage through physical examinations, blood tests, and advanced imaging tools such as X-rays and MRI scans. Unlike standard wound care, orthopedic intervention focuses on preserving mobility, preventing long-term disability, and ensuring structural stability of the affected limb. By determining whether bone tissue is infected or compromised, orthopedic doctors can design a treatment plan that minimizes the risk of amputation. Their expertise also extends to recommending supportive devices that help patients maintain independence during recovery. Patients who rely solely on general wound care may not receive the specialized evaluation needed to determine whether the bone or joint structure is at risk. Orthopedic care bridges this gap by addressing both infection management and musculoskeletal preservation, making it a vital component of treatment.
Common Orthopedic Treatment Options for Diabetic Gangrene
Several orthopedic treatment methods are used depending on the severity and spread of the condition. Surgical debridement is one of the most common approaches, where dead or infected tissue is removed to stop the progression of gangrene. This procedure often improves circulation and gives surrounding healthy tissue a chance to recover. In more advanced cases, amputation may be necessary to protect the patient’s life, but orthopedic surgeons aim to preserve as much function and mobility as possible. Techniques such as partial foot amputation, toe removal, or below-the-knee surgery are carefully planned to optimize prosthetic fitting later. Bone resection procedures may be performed when infection has spread to the skeletal system but can be controlled without full amputation. In some cases, reconstructive surgeries involving grafts or orthopedic implants restore stability and help patients regain mobility. Rehabilitation and physical therapy follow these interventions to ensure patients adjust physically and emotionally while preventing complications.
Integrating Multidisciplinary Approaches with Orthopedic Treatment
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene rarely works in isolation. Instead, it is most effective when combined with a multidisciplinary approach that brings together vascular surgeons, endocrinologists, podiatrists, and wound care specialists. Vascular surgeons may restore blood flow through bypass surgery or angioplasty, which complements orthopedic efforts to preserve limbs. Endocrinologists focus on blood sugar control, as uncontrolled diabetes directly impacts wound healing and increases infection risk. Podiatrists and wound care nurses contribute by monitoring and maintaining the condition of the feet and lower legs during recovery. In addition, advanced treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy and modern wound dressings are often used alongside orthopedic procedures to accelerate healing. Antibiotic therapies are also crucial in cases where bacterial infection plays a role in tissue death. This collaborative approach ensures that all aspects of the patient’s health are addressed, leading to better long-term outcomes. Patients benefit not only from orthopedic expertise but also from a system of support that tackles the root causes of gangrene.
Preventive Orthopedic Care for Diabetic Patients
Preventing diabetic gangrene begins with proactive measures, and orthopedic care plays a key role in this process. Regular screenings help detect early warning signs of reduced blood flow or bone problems, allowing interventions before gangrene develops. Orthopedic specialists often recommend protective footwear, custom insoles, and supportive devices that reduce pressure on vulnerable areas of the feet. Patients are advised to inspect their feet daily for blisters, cuts, or signs of infection that may progress unnoticed due to diabetic neuropathy. Lifestyle modifications are equally important, including regular physical activity to improve circulation, dietary changes to manage blood sugar, and smoking cessation to protect blood vessel health. Orthopedic clinics may also provide education on safe exercise routines and mobility aids that reduce injury risks. By engaging in preventive orthopedic care, patients not only reduce their chances of developing gangrene but also strengthen their overall musculoskeletal health. This proactive approach significantly lowers the need for invasive treatments later on.
Recovery and Quality of Life After Orthopedic Treatment
Recovery from diabetic gangrene involves more than just medical intervention; it requires ongoing support to restore physical and emotional well-being. After orthopedic treatment, patients typically undergo physical rehabilitation to rebuild strength, restore balance, and adapt to changes in mobility. Rehabilitation specialists help patients relearn walking techniques, often with assistive devices or prosthetics when amputations are involved. Emotional support is also vital, as many patients struggle with anxiety, depression, or fear of recurrence after treatment. Counseling, support groups, and family involvement make recovery smoother and more sustainable. Orthopedic professionals remain involved by monitoring long-term bone and joint health, preventing new complications, and adjusting mobility solutions as needed. For those who undergo amputation, advanced prosthetic technology and orthopedic expertise provide opportunities to regain independence and maintain an active lifestyle. Ultimately, orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene not only saves lives but also improves quality of life by giving patients the ability to function and thrive despite their diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the first signs of diabetic gangrene that require medical attention?
The earliest signs include skin discoloration, swelling, foul odor, numbness, and persistent pain in the affected area. Patients should seek immediate medical care if these symptoms appear.
Can orthopedic treatment save a limb affected by diabetic gangrene?
Yes, in many cases orthopedic treatment combined with other medical approaches can save a limb. Early intervention improves the chances of avoiding major amputation.
When is amputation necessary, and how is it planned?
Amputation becomes necessary when infection or tissue death cannot be controlled by other treatments. Orthopedic surgeons plan amputations carefully to preserve as much mobility and limb length as possible.
How does orthopedic care differ from standard wound care in diabetic gangrene?
While wound care focuses on surface healing and infection control, orthopedic care addresses deeper issues involving bones, joints, and mobility preservation. This makes it essential for long-term outcomes.
What preventive steps should diabetic patients take to avoid gangrene?
Patients should maintain stable blood sugar, inspect their feet daily, wear protective footwear, avoid smoking, and consult orthopedic specialists for regular screenings.
What role does rehabilitation play after orthopedic treatment for gangrene?
Rehabilitation restores strength, balance, and independence. It also helps patients adjust to lifestyle changes and provides strategies for preventing future complications.
Are there long-term orthopedic solutions for patients who undergo amputation?
Yes, prosthetic devices, supportive orthopedic implants, and mobility aids allow patients to regain independence. Regular orthopedic follow-ups ensure continued adaptation and quality of life.